The Purchase-to-Pay process is an end-to-end process that starts with a requisition order and ends up with the payment of the supplier's invoice. The Purchase-to-Pay process consists of steps such as: Creating & approving the purchase requisition, creating, approving & closing the purchase order, receiving the goods, creating & approving the invoice and executing the outgoing payment.
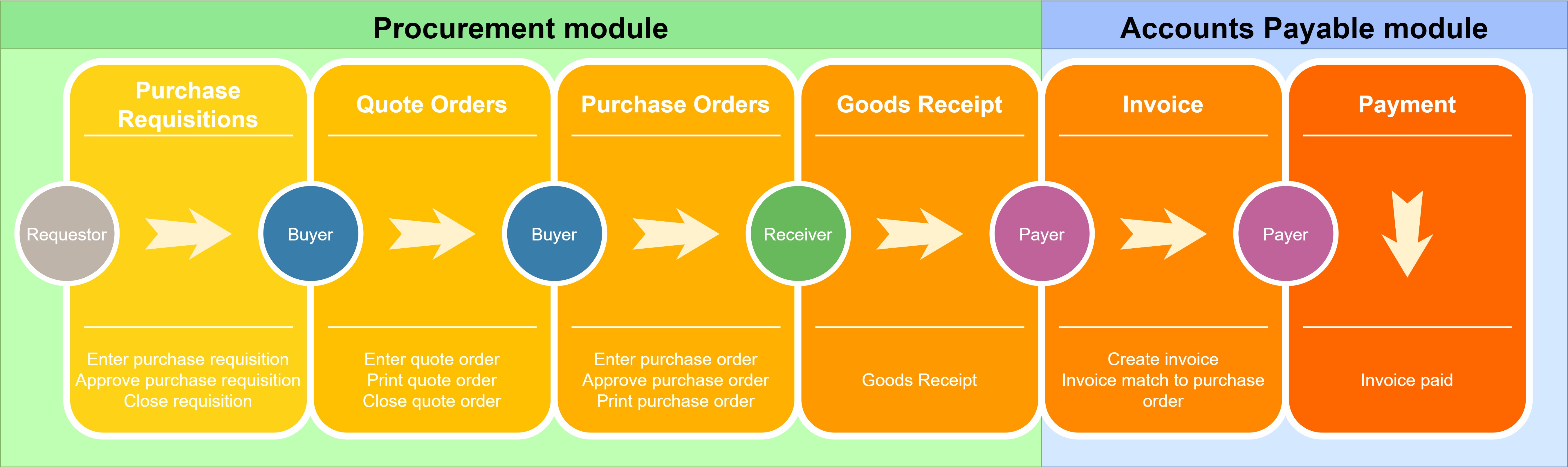
The Procurement module includes all steps related to orders for any of the following type:
The Accounts Payable module includes the following objects:
With the Oracle JDE Purchase-to-Pay app template you can create process apps that give insight in how your Purchase-to-Pay process actually performs. For example, how long it takes for a purchase request to become an actual Purchase Order, how long it takes to process the Purchase Orders, and most important to what extent are you paying in time. For all steps in the process, Purchase-to-Pay provides insights into the throughput times.
The Oracle JDE modules Procurement and Accounts payable are mandatory. Other tables could be used for master data purposes.
To connect via CData, the user establishing the connection must have appropriate read permissions on each of the objects which are being extracted. All fields included in the input tables must be visible for the user extracting the data.
Below is a description on how to use CData Sync to set up a source connection and load data into a Process Mining Oracle JDE Purchase-to-Pay process app.
In general, you should follow the steps as described in Loading data using CData Sync (Snowflake) or Loading data using CData Sync (SQL Server) to set up data loading using CData Sync. Since specific settings are required when using Oracle JDE, pay attention to the steps described below.
Define the following settings in the Replicate Options section in the Advanced tab in the Job Settings panel.
Important: Make sure you edit the Pre-job Event.
CData Sync allows the use of environment variables in order to drive specific extraction logic in each query.
| Variable | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| start_extraction_date | Defines first date for which data will be extracted. | Mandatory |
| end_extraction_date | Last date for which data will be extracted. |
Be mindful of choosing a start_extraction_date that encompasses the data that you want to capture, as orders are the starting point of the order to cash process.
In order to setup the environment variables:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Go to the JOBS tab and open the extraction job created in 4: Creating the extraction job. |
| 2 | Go to the Events tab in the Job Settings panel. |
| 3 | Edit the Pre-Job Event section to add the code displayed below after <!-- Code goes here -- >. |
| 4 | Click on Save Changes. |
<!-- Modify environment variables here. -->
<!-- Variable start_extraction_date and end_extraction_date must be populated.-->
<!-- The following values are just an example (start being = 01-01-1900 and end being = 01-01-2300).-->
<api:set attr="out.env:start_extraction_date" value= 000001 />
<api:set attr="out.env:end_extraction_date" value= 400001 />
<api:push item="out" />
Important: Do not modify the api:info details that are shown by default.
In order to modify the environment variables, modify the values within the Events tab. By default, end_extraction_date will default to today's date. start_extraction_date must always be populated using JDE julian format. Use the following to calculate the correct value:
To transform 31/12/2021 into a JDE julian format (CYYDDD is an integer) C = First 2 digits from the year minus the 19 (JDE uses 01-01-1900 as base to create date fields), in our example: C = 20 - 19 = 1 YY = The last 2 digits of the year, in our example: YY = 21 DDD = Is the day of the year (1-365 range, except for leap years that is 1-366), in our example: DDD = 365 So 31/12/2021 in JDE format is 121365.
Once the job is correctly setup, click on Add Custom Query under the Tables tab and paste the following queries (each query needs to maintain the semicolon at the end). Make sure you save all changes.
Default Extraction
REPLICATE [F0005_raw] SELECT [DRKY] AS [drky], [DRRT] AS [drrt], [DRSY] AS [drsy], [DRDL01] AS [drdl01] FROM [JDECTL920].[F0005];
REPLICATE [F0006_raw] SELECT [MCMCU] AS [mcmcu], [MCDL01] AS [mcdl01] FROM [JDEDATA920].[F0006];
REPLICATE [F0010_raw] SELECT [CCCO] AS [ccco], [CCCRCD] AS [cccrcd], [CCNAME] AS [ccname] FROM [JDEDATA920].[F0010];
REPLICATE [F0014_raw] SELECT [PNPTC] AS [pnptc], [PNPTD] AS [pnptd] FROM [JDEDATA920].[F0014];
REPLICATE [F0015_raw] SELECT [CXAN8] AS [cxan8], [CXCRCD] AS [cxcrcd], [CXCRDC] AS [cxcrdc], [CXRTTYP] AS [cxrttyp], [CXEFT] AS [cxeft], [CXCRR] AS [cxcrr] FROM [JDEDATA920].[F0015] WHERE ([CXEFT] >= '{env:start_extraction_date}') AND ([CXEFT] <= '{env:end_extraction_date}');
REPLICATE [F0092_raw] SELECT [ULAN8] AS [ulan8], [ULUSER] AS [uluser] FROM [JDESY920].[F0092];
REPLICATE [F0101_raw] SELECT [ABAN8] AS [aban8], [ABALPH] AS [abalph], [ABMCU] AS [abmcu], [ABAT1] as [abat1] FROM [JDEDATA920].[F0101];
REPLICATE [F0116_raw] SELECT [ALAN8] AS [alan8], [ALEFTB] AS [aleftb], [ALCTY1] AS [alcty1], [ALCOUN] AS [alcoun], [ALADDS] AS [aladds], [ALCTR] AS [alctr] FROM [JDEDATA920].[F0116];
REPLICATE [F0411_raw] SELECT [RPDOC] AS [rpdoc], [RPDCT] AS [rpdct], [RPKCO] AS [rpkco], [RPDCTA] AS [rpdcta], [RPSFX] AS [rpsfx], [RPAN8] AS [rpan8], [RPVOD] AS [rpvod], [RPTORG] AS [rptorg], [RPAAP] as [rpaap], [RPBCRC] AS [rpbcrc], [RPAG] AS [rpag], [RPCRCD] AS [rpcrcd], [RPACR] AS [rpacr], [RPPTC] AS [rpptc], [RPPYIN] AS [rppyin], [RPUPMJ] AS [rpupmj], [RPDICJ] AS [rpdicj], [RPDIVJ] AS [rpdivj], [RPDGJ] AS [rpdgj], [RPDDJ] AS [rpddj], [RPDDNJ] AS [rpddnj], [RPADSC] AS [rpadsc], [RPADSA] AS [rpadsa] FROM [JDEDATA920].[F0411] WHERE ([RPUPMJ] >= '{env:start_extraction_date}') AND ([RPUPMJ] <= '{env:end_extraction_date}');
REPLICATE [F0414_raw] SELECT [RNPYID] AS [rnpyid], [RNKCO] AS [rnkco], [RNDOC] AS [rndoc], [RNDCT] AS [rndct], [RNDCTM] AS [rndctm], [RNUSER] AS [rnuser], [RNPID] AS [rnpid], [RNAN8] AS [rnan8], [RNRC5] AS [rnrc5], [RNUPMJ] AS [rnupmj] FROM [JDEDATA920].[F0414] WHERE ([RNUPMJ] >= '{env:start_extraction_date}') AND ([RNUPMJ] <= '{env:end_extraction_date}') AND [RNDCT] IS NOT NULL;
REPLICATE [F4101_raw] SELECT [IMDSC1] AS [imdsc1], [IMLITM] AS [imlitm] FROM [JDEDATA920].[F4101];
REPLICATE [F40203_raw] SELECT [FSDCTO] AS [fsdcto], [FSTRTY] AS [fstrty], [FSSTDS] AS [fsstds], [FSLNTY] AS [fslnty] FROM [JDEDATA920].[F40203];
REPLICATE [F43121_raw] SELECT [PRMATC] AS [prmatc], [PRKCO] AS [prkco], [PRDOC] AS [prdoc], [PRDCT] AS [prdct], [PRKCOO] AS [prkcoo], [PRDOCO] AS [prdoco], [PRDCTO] AS [prdcto], [PRLNID] AS [prlnid], [PRAN8] AS [pran8], [PRSFXO] AS [prsfxo], [PRNLIN] AS [prnlin], [PRLITM] AS [prlitm], [PRUOM] AS [pruom], [PRUREC] AS [prurec], [PRAREC] AS [prarec], [PRCRCD] AS [prcrcd], [PRFEC] AS [prfec], [PRUPMJ] AS [prupmj], [PRTDAY] AS [prtday], [PRUSER] AS [pruser], [PRPID] AS [prpid] FROM [JDEDATA920].[F43121] WHERE ([PRUPMJ] >= '{env:start_extraction_date}') AND ([PRUPMJ] <= '{env:end_extraction_date}') AND [PRMATC] IN ('2','3');
REPLICATE [F43199_raw] SELECT [OLOPDJ] AS [olopdj], [OLAEXP] AS [olaexp], [OLFEA] AS [olfea], [OLSHAN] AS [olshan], [OLKCOO] AS [olkcoo], [OLDOCO] AS [oldoco], [OLDCTO] AS [oldcto], [OLLNID] AS [ollnid], [OLOCTO] AS [olocto], [OLMCU] AS [olmcu], [OLPDS1] AS [olpds1], [OLPDS2] AS [olpds2], [OLPDP1] AS [olpdp1], [OLPDP2] AS [olpdp2], [OLLITM] AS [ollitm], [OLAN8] AS [olan8], [OLLNTY] AS [ollnty], [OLCRCD] AS [olcrcd], [OLUORG] AS [oluorg], [OLUOPN] AS [oluopn], [OLUOM] AS [oluom],
[OLTRDJ] AS [oltrdj], [OLDGL] AS [oldgl], [OLLTTR] AS [ollttr], [OLNXTR] AS [olnxtr], [OLUPMJ] AS [olupmj], [OLTDAY] AS [oltday], [OLUSER] AS [oluser], [OLTORG] AS [oltorg], [OLPID] AS [olpid], [OLOKCO] AS [olokco], [OLOORN] AS [oloorn], [OLOGNO] AS [ologno], [OLDRQT] AS [oldrqt], [OLUKID] AS [olukid], [OLLOCN] AS [ollocn] FROM [JDEDATA920].[F43199] WHERE ([OLUPMJ] >= '{env:start_extraction_date}') AND ([OLUPMJ] <= '{env:end_extraction_date}') AND [OLLTTR] IS NOT NULL;
The following tables include the list of fields per input table, their description, data type to be used when formatting the input and the filter flag to identify those that are being used to filter data.
Below is an overview of the different field types and their default format settings.
| Field type | Description |
|---|---|
| boolean | true, false, 1, 0 |
| date | CYYDDD |
| double | Decimal separator: . (dot); thousand separator: none |
| integer | Thousand separator: none |
| text | N/A |
Notes
Stores user-defined codes and their descriptions.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| drsy | Product Code | text | The concatenation between Product code and User Defined Codes is used for filtering. Valid values are '00CN', '00DT', '00PY', '00S', '00UM', '01ST', '41P1', '41P2', '41S1', '41S2' |
| drrt | User Defined Codes | text | See comment above. |
| drky | User Defined Code | text | |
| drdl01 | Description | text |
Stores information about branch, plant, warehouse, and business unit information, such as company, description, and category codes that are assigned to that entity.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| mcmcu | Business unit | text | |
| mcdl01 | Description | text |
Stores company definitions, including number and name, fiscal date pattern, and current period.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| ccco | Company | text | |
| cccrcd | Currency code from | text | |
| ccname | Name | text |
Stores standard payment terms.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| pnptc | Payment terms code | text | |
| pnptd | Description payment terms | text |
Stores currency exchange rates.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| cxan8 | Address number | text | |
| cxcrcd | Currency code from | text | |
| cxcrdc | Currency code to | text | |
| cxrttyp | Currency rate type | text | |
| cxeft | Date effective | date | Main field used for time-based filtering |
| cxcrr | Currency conversion rate spot rate | double |
Stores information about the user and what kinds of access the user has.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| ulan8 | Address number | text | |
| uluser | User id | text |
Stores address book information, including companies, suppliers, and customers.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| aban8 | Address number | text | |
| abalph | Name | text | |
| abmcu | Business unit | text | |
| abat1 | Search type | text |
Stores addresses, address lines, postal codes, and effective dates for address book numbers. Also, the stored information includes the fields that need to be protected for data privacy.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| alan8 | Address number | text | |
| aleftb | Date effective | date | |
| alcty1 | City | text | |
| alcoun | County | text | |
| aladds | State | text | |
| alctr | Country | text |
Stores basic information about each item, including Item number, Description, Search keys Category codes, Default units of measure, Process groups for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Warehouse Management system, Item dimension group.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| imdsc1 | Description | text | |
| imlitm | Long item number | text |
Stores information about order activity rules, such as order type, line type, last status, and next status.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| fsdcto | Order type | text | |
| fstrty | Status line | integer | |
| fsstds | Description status | text | |
| fslnty | Line type | text |
Stores information about Accounts Payable Ledger.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| rpdoc | Document | text | |
| rpdct | Document type | text | |
| rpkco | Document company | text | |
| rpdcta | Document type adjusting | text | |
| rpsfx | Document pay item | text | |
| rpan8 | Address number | text | |
| rpvod | Void flag | text | |
| rptorg | Transaction originator | text | |
| rpaap | Amount open | double | |
| rpbcrc | Currency code base | text | |
| rpag | Amount gross | double | |
| rpcrcd | Currency code from | text | |
| rpacr | Amount currency | double | |
| rpptc | Payment terms code | text | |
| rppyin | Payment instrument | text | |
| rpupmj | Date updated | date | Main field used for time-based filtering |
| rpdicj | Date batch julian | date | |
| rpdivj | Date invoice | date | |
| rpdgj | Date general ledger | date | |
| rpddj | Date net due | date | |
| rpddnj | Date discount due | date | |
| rpadsc | Discount available | double | |
| rpadsa | Discount taken | double |
Stores information about Accounts Payable Matching Document Detail.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| rnpyid | Payment id | text | |
| rnkco | Document company | text | |
| rndoc | Document | text | |
| rndct | Document type | text | This field cannot be null or blank |
| rndctm | Document type matching | text | |
| rnuser | User id | text | |
| rnpid | Program id | text | |
| rnan8 | Address number | text | |
| rnrc5 | File line identifier 5 0 | text | |
| rnupmj | Date updated | date | Main field used for time-based filtering |
Stores receipt record and voucher record information with details such as open quantity and open amount.
| Field | Stores | Type | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| prmatc | Type match record type | integer | Filter by 2 and 3 |
| prkco | Document company | text | |
| prdoc | Document voucher invoice | text | |
| prdct | Document type | text | |
| prkcoo | Order company | text | |
| prdoco | Document | text | |
| prdcto | Order type | text | |
| prlnid | Line number | text | |
| pran8 | Address number | text | |
| prsfxo | Order suffix | text | |
| prnlin | Number of lines | text | |
| prlitm | Long item number | text | |
| pruom | Unit of measure | text | |
| prurec | Units received | double | |
| prarec | Amount received | double | |
| prcrcd | Currency code from | text | |
| prfec | Amount received foreign | double | |
| prupmj | Date updated | date | Main field used for time-based filtering |
| prtday | Time of day | integer | |
| pruser | User id | text | |
| prpid | Program id | text |
Stores detail information for each purchase order line, such as item number, price, quantity ordered, and purchase amount (PA) ledger type.
| Field | Stores | Field | Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|
| olopdj | Date original promised delivery | date | |
| olaexp | Amount extended price | double | |
| olfea | Amount foreign extended price | double | |
| olshan | Address number ship to | text | |
| olkcoo | Order company | text | |
| oldoco | Document | text | |
| oldcto | Order type | text | |
| ollnid | Line number | text | |
| olocto | Original order type | text | |
| olmcu | Business unit | text | |
| olpds1 | Reporting code1 sales | text | |
| olpds2 | Reporting code2 sales | text | |
| olpdp1 | Reporting code1 purchasing | text | |
| olpdp2 | Reporting code2 purchasing | text | |
| ollitm | Long item number | text | |
| olan8 | Address number | text | |
| ollnty | Line type | text | |
| olcrcd | Currency code from | text | |
| oluorg | Units order quantity | integer | |
| oluopn | Units open | integer | |
| oluom | Unit of measure as input | text | |
| oltrdj | Date order | date | |
| oldgl | Date general ledger | date | |
| ollttr | Status code last | text | |
| olnxtr | Status code next | text | |
| olupmj | Date updated | date | Main field used for time-based filtering |
| oltday | Time of day | integer | |
| oluser | User id | text | |
| oltorg | Transaction originator | text | |
| olpid | Program id | text | |
| olokco | Document company | text | |
| oloorn | Original order number | text | |
| ologno | Original line number | text | |
| oldrqt | Requested delivery time | integer | |
| olukid | Unique key id | text | |
| ollocn | Location | text |
| Entity | Transactional tables | Master data tables |
|---|---|---|
| Purchase requisitions | F43199 | F0005, F0010, F0015, F0092, F0101, F4101 |
| Purchase orders | F43199 | F0005, F0010, F0092, F0101, F0116 |
| Purchase order items | F43199 | F0005, F0006, F0010, F0015, F0092, F0101, F4101 |
| Goods receipt | F43199 | |
| Invoice | F43121, F0411 | F0005, F0010, F0014, F0092, F0101 |
| Invoice item | F43121, F0411 | F0005, F0015, F4101 |
| Accounting documents | F43121, F0411 | |
| Payments | F0411, F0414 |
For the Procurement module, activities are generated from a concatenation of the last status and its description which are not standard and mostly customizable for each JDE implementation.
Procurement activities: F43199.Status_Code_Last + ' - ' + F40203.Description_Status
Examples:
105 - Create New Item
105 - Reject Requisition
Below is a list of activities that can exist for the Procurement module. (Note that the actual names depend on the JDE implementation)
The Accounts Payable module does not have historical information nor customized activities like mentioned for Procurement. Therefore, all activities were created in advance.
The following activities are available for both Procurement and Accounts Payable modules:
| Activity | Activity code | Transactional table | Master data table |
|---|---|---|---|
| Approve purchase order header | APPROVE_PO | F43199 | F0005, F0006, F0092, F0101, Setup_activities, Setup_users |
| Change invoice value | F43121, F0411 | F0005, F0006, F0010, F0092, F0101, Setup_activities, Setup_users | |
| Create invoice header | CREATE_INVOICE | F43121, F0411 | F0005, F0006, F0092, F0101, Setup_activities, Setup_users |
| Create invoice item | CREATE_INVOICE_ITEM | F43121, F0411 | F0005, F0006, F0010, F0092, F0101, Setup_activities, Setup_users |
| Create purchase order header | CREATE_PO | F43199 | F0005, F0006, F0092, F0101, Setup_activities, Setup_users |
| Gain/Loss on Exchange Rate | F0414 | F0005, F0006, F0092, F0101, Setup_activities, Setup_users | |
| Invoice match to PO | F43121 | F0005, F0006, F0092, F0101, Setup_activities, Setup_users | |
| Invoice paid | CREATE_OUTGOING_PAYMENT | F0414 | F0005, F0006, F0092, F0101, Setup_activities, Setup_users |
| Payment void | F0414 | F0005, F0006, F0092, F0101, Setup_activities, Setup_users | |
| Reverse invoice item | F43121, F0411 | F0005, F0006, F0010, F0092, F0101, Setup_activities, Setup_users | |
| Reverse invoice match to PO | F43121 | F0005, F0006, F0092, F0101, Setup_activities, Setup_users |
Note on Activity_order attribute Activity orders are set following different logics according to the module where they were generated. For all activities from procurement module, the last status code is used as the activity order. For AP activities, they were predefined in the models that generate them.
The following table shows the ranges used for each entity in the procurement module.
| Entity of the activity | Minimum activity order number | Maximum activity order number |
|---|---|---|
| Purchase requisitions orders | 100 | 120 |
| Quote orders | 140 | 160 |
| Blanket orders | 209 | 215 |
| Purchase orders | 219 | 399 |
| Goods receipt | 400 | 400 |
| Cancellations or purges of any type of order | 900 | 999 |
The following is the complete list of all Accounts Payable activities and their Activity order.
| Activity | Activity order |
|---|---|
| Create invoice header | 1099 |
| Create invoice item | 1100 |
| Invoice match to PO | 1150 |
| Reverse invoice match to PO | 1151 |
| Change invoice value | 1200 |
| Invoice Paid | 1400 |
| Gain/Loss on Exchange Rate | 1401 |
| Payment Void | 1450 |
| Reverse invoice item | 1500 |
The procurement module in JDE records transactions for all types of orders in the same table F43199 and there is no classification done in the system that could be used for splitting between all entities. Therefore, knowing what type of orders belong to each entity needs an extra effort. P2p_entity_list will be used to automatically classify all order types into different entities.
The last_status_code in JDE is used for tracking the activities that have happened to each order item. These statuses are 3-digit numbers that go from 100 to 999. And, in a standard implementation of JDE, sections of that range are defined for each entity.
| Entity | Min Last Status | Max Last Status |
|---|---|---|
| Purchase Requisition | 100 | 120 |
| Quote Order | 140 | 160 |
| Blanket Order | 210 | 215 |
| Purchase Order | 220 | 400 |
All statuses greater than 900 do not represent any particular entity and must be filtered out. Statuses over 900 are related to cancellations and purges.
Seed files can be used for variables that require a list of values. Seed files are available in the seeds folder of the app transformations. You can edit the seeds files when editing app transformations.
The following seed files are available for Oracle JDE Purchase-to-Pay:
Setup_activities.csv
| Field | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activity_name | varchar(50) | The name of the activity; it is generated automatically | 100 - Enter Purchase Requisition |
| Activity_category | varchar(50) | The type of activity that takes place | Change, Set block, Remove block or NULL |
| Activity_code | varchar(50) | The code for the activity that takes place used to define metrics and tags in the Purchase-to-Pay Discovery Accelerator | CREATE_PR |
| Automated_flag | varchar(1) | 1, 0, or blank. The value 1 identifies automated activities | 1 |
Setup_order_types.csv
As Oracle JDE stores all type of orders in the same table, it is required to classify each of them into entities.
For remote cases where one of the order types could not be classified automatically, the following message is displayed in the P2p_entity_list table: Order type not defined in a single entity.
In this case, the order type must be classified manually by adding it to the setup_order_type file.
| Field | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Order_type | varchar(2) | Order type code. These are defined on each JDE implementation and they can widely vary | YK, PO, PR |
| Entity_override | varchar(50) | Entity to which the order type must belong to. Possible values are: 'Purchase Requisition', 'Quote Order', 'Blanket Order', 'Purchase Order' | Purchase Order |
Setup_users.csv
There are not always automated flags or ways to use algorithms to find out what activities were made automatically. In this case, you can manually set those users that are deemed automated.
The setup_users.csv seed file contains the information of all automated users that need to be flagged manually.
| Field | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| User_id | varchar(10) | User id as stored in transactional tables | ERMAC123 |
| Automated_flag | varchar(1) | 1, 0, or blank. The value 1 identifies automated users | 1 |
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| date_format | string / Integer | Specifies the date format which will be used when converting to Date type. SQL Server format value is 112. Snowflake format value is 'YYYYMMDD'. |
| datetime_format | string / Integer | Specifies the date format which will be used when converting to DateTime type. SQL Server format value is 20. Snowflake format value is 'YYYY-MM-DD hh24:mi:ss.ff3'. |
| display_currency | string | Currency code used for all "value" attributes. All amounts (Values) will be converted to the selected display_currency. It is suggested to select the reporting currency code of the client |
| material_group_field | string | Selection of the most representative category field to populate material_group attribute in requisition and PO entities. Available values are: 'Reporting_code1_purchasing', 'Reporting_code2_purchasing', 'Reporting_code1_sales' and 'Reporting_code2_sales'. This is something that need to be decided alongside the client to select the most representative value |
Display currency: In the rare case where the client does not have the same reporting currency code across its multiple companies, it may happen that currency conversion rates are not available for converting everything into a single currency.
Order types not being classified in any entity: If one of the values of the P2p_entity_list.Entity is 'Order type not defined in a single entity' a manual intervention must be done.